Experience the ancient art of acupressure therapy
What is Acupressure?
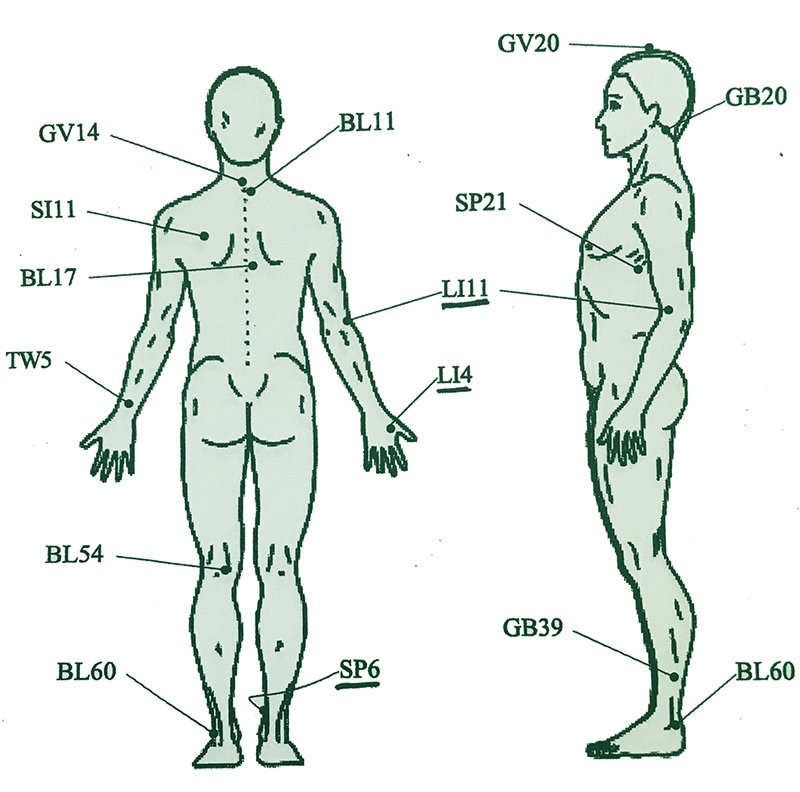
Acupressure is a traditional healing technique rooted in Chinese medicine. It involves applying finger pressure to key points along the body’s meridians (energy pathways) to stimulate the body's natural healing abilities. Unlike acupuncture, acupressure is non-invasive and does not involve needles.
Acupressure therapy is a holistic healing practice that promotes natural wellness and balance in your body. Acupressure uses gentle pressure on specific points to release tension, improve circulation, and restore energy flow.